What’s Flavonoids: A Comprehensive and Detailed Review
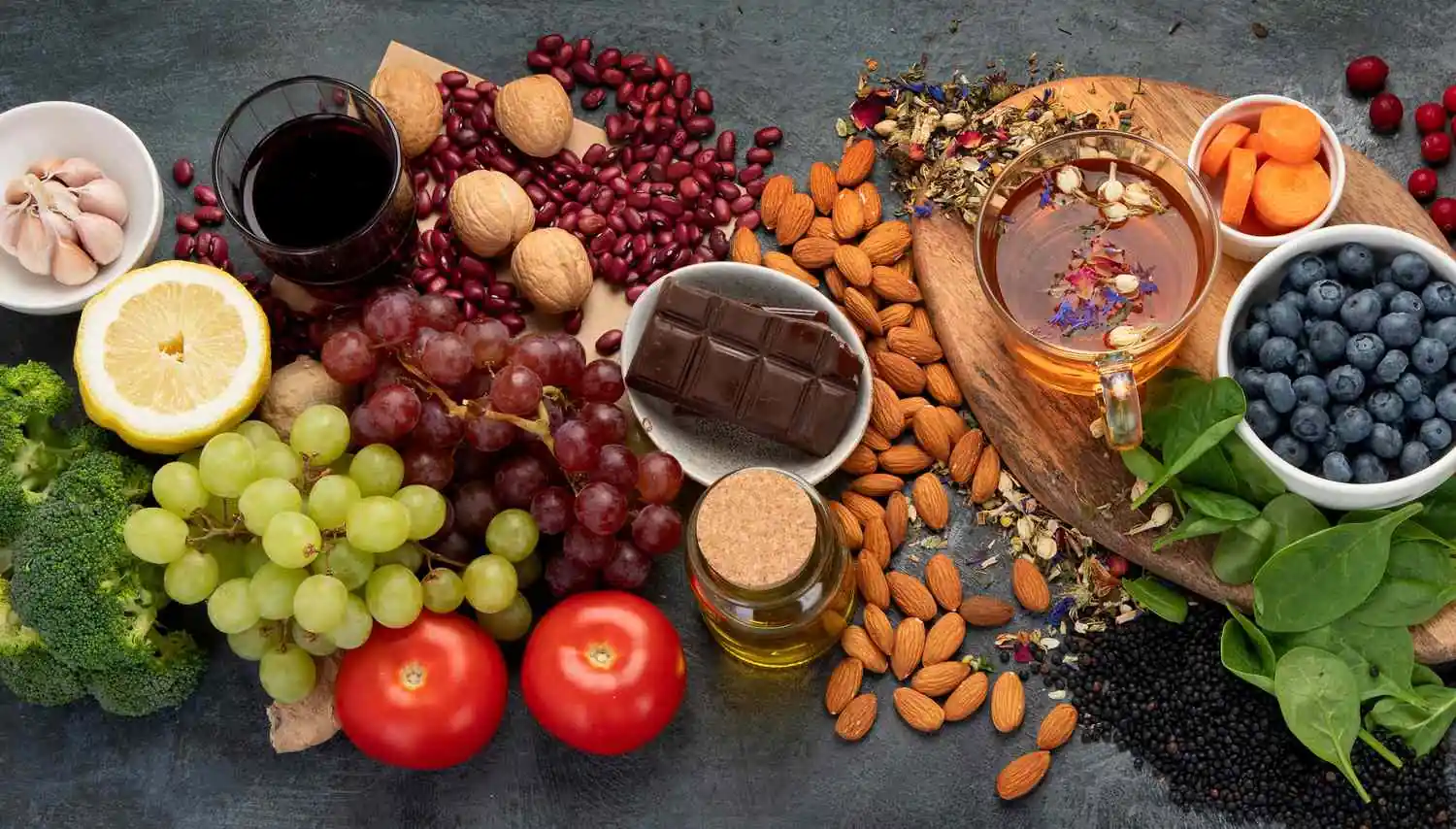

There are numerous foods that are said to have a high flavonoid content. What’s flavonoids, and why are they good for your health? Which foods and beverages are particularly rich in these compounds? What are flavonoid supplements that are worth buying?
Read on, and you will find the answers to all these and numerous other questions.
Flavonoids: What Are They
Flavonoids (also called bioflavonoids) are a subclass of polyphenols, complex organic compounds that are abundant in plants. Both polyphenols and flavonoids feature several ring-shaped phenol units: because of their complex structure, these compounds serve numerous biological functions. Plants use bioflavonoids to attract insects and speed up pollination, as well as to combat microbial infections and regulate cell growth.

What Do Flavonoids Do for the Body?
Bioflavonoids can help your health in a number of ways:
- In vitro (test tube) studies have demonstrated that these compounds are extremely effective at binding free radicals (aggressive chemicals that can do harm to the cells of your body and speed up aging);
- Bioflavonoids can chelate (bind) metal ions such as iron and copper;
- There are numerous studies that demonstrate that various flavonoid subclasses can reduce inflammation;
- Bioflavonoids are known to slow down atherosclerosis development and reduce the rate of arteries clogging by platelets;
- They help the production of nitric oxide, a compound that is directly responsible for blood pressure normalization;
- They additionally help blood pressure reduction by inhibiting enzymes that prevent relaxation of blood vessels;
- These compounds also improve insulin secretion and reduce hyperglycemia;
- The above-mentioned antioxidant action and regulation of DNA repair make bioflavonoids a good choice for cancer prevention;
- There is also a promising hypothesis that flavonoids can boost cognitive function and reduce neuroinflammation.

Benefits for the Health
Ongoing research confirms the above-described beneficial health effects of consuming flavonoids:
- All five subgroups of bioflavonoids were demonstrated to have a marked effect on lowering blood pressure in a 2015 study;
- Another 2015 study demonstrates that people who get high quantities of bioflavonoids from their diets have a lower risk of a cardiovascular event;
- According to a 2018 meta-analysis, consuming a diet rich in flavonoids may be associated with a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A 2011 review lists the evidence of flavonoids being able to stop cancer cells from multiplying.

What Are the Best Foods Rich in Flavonoids
Having answered the question, what are flavonoids and what do they do, let us list the main five subtypes of these compounds and name the foods that are particularly rich in them.
Flavanols
Flavanols are famous for their antioxidant properties and can be used to improve symptoms of cardiovascular disease. Here are the foods that are rich in them:
| Food | Flavanols content, mg per 100 grams |
| Onions, raw | 27.1 |
| Onions, boiled | 24.7 |
| Apples (with skin) | 6.0 |
| Black tea (brewed) | 3.8 |
| Beer | 0.9 |
| Tomatoes, red | 0.8 |

Flavan-3-ols
Tea (especially green tea) is an excellent source of these flavonoid compounds, while dark chocolate and blueberries are also very good choices.
| Food | Flavan-3-ols content, mg per 100 grams |
| Cocoa powder | 243,2 |
| Green tea (brewed) | 203,0 |
| Black tea (brewed) | 115,3 |
| Blueberries | 51,7 |
| Dark chocolate | 50,0 |
| Milk chocolate | 14,2 |
| Peaches | 9,2 |
| Apples (with skin) | 8,1 |
| Pears | 6,8 |
| Bananas | 6,1 |
| Apple juice | 6,0 |
| Strawberries | 4,6 |
| Beer | 2,5 |

Flavones
Blue and white flowering plants contain flavonoid pigments called flavones, which also function as natural pesticides, shielding leaves from harmful insects. Flavones are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and can be found in:
| Food | Flavones content, mg per 100 grams |
| Parsley, dried | 13,525.9 |
| Parsley, raw | 227.2 |
| Chili pepper, raw | 5.3 |
| Bell pepper, green, raw | 5.0 |
| Oranges | 1.1 |
| Watermelon | 0.6 |
| Cantaloupe | 0.6 |
| Apples (with skin) | 0.5 |

Flavanones
Well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties, flavanones are also believed to aid in weight and cholesterol management. You can find them in these foods:
| Food | Flavanones content, mg per 100 grams |
| Lemons, peeled | 49.8 |
| Oranges, peeled | 42.6 |
| Orange juice | 29.5 |
| Lemon juice | 24.0 |
| Grapefruit juice | 19.2 |
| Tangerines | 18.0 |
| Tomatoes, red | 0.7 |

Anthocyanins
The red, purple, and blue hues of flowers are the result of naturally occurring flavonoid pigments called anthocyanins. These compounds are mostly concentrated in the outer skin of berries:
| Food | Anthocyanins content, mg per 100 grams |
| Blueberries | 163,5 |
| Cranberries | 92,0 |
| Sweet cherries | 80,2 |
| Cabbage, red, raw | 73,0 |
| Raspberries | 38,7 |
| Strawberries | 33,6 |
| Black beans, cooked | 28,0 |
| Pears | 12,3 |
| Plums | 12,0 |
| Bananas | 7,4 |
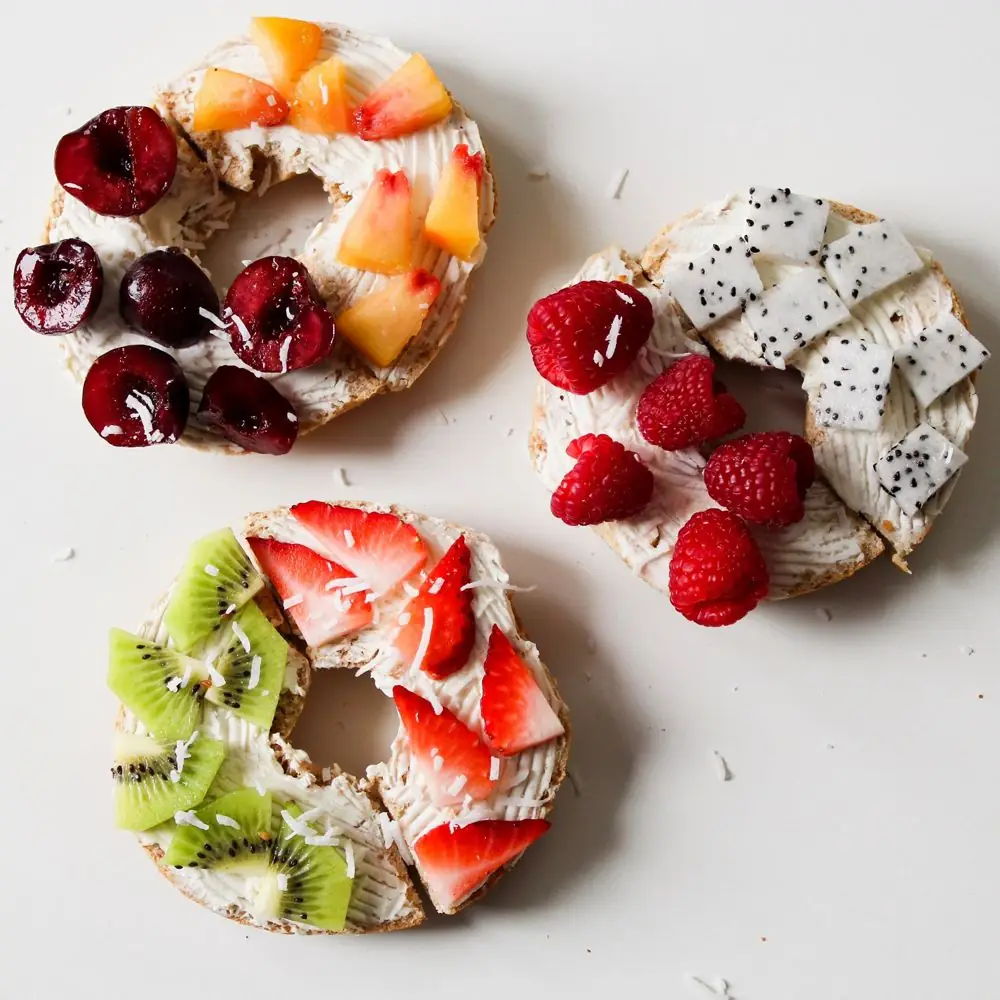

So, which foods are highest in flavonoids? Parsley (both raw and dried), tea (both green and black), blueberries, onions, citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), cranberries, cherries, red cabbage, raspberries, and strawberries are all excellent sources of these beneficial compounds.
Even if you like coffee better than tea, enjoying several cups of green tea during your day is always a good idea — and don’t forget to use copious amounts of parsley when cooking!
Why Are Supplements with Flavonoids Important
There are numerous dietary supplements that feature all subclasses of bioflavonoids in very high concentrations.
In laboratory tests it was found that eating foods rich in bioflavonoids does not necessarily lead to higher concentrations of these compounds in the bloodstream: it is very likely that the only way to fully enjoy the antioxidant benefits of flavonoids is to get extremely high amounts of them from dietary supplements.
What’s more, as bioflavonoids usually have low bioavailability and are quickly removed from the bloodstream, using higher doses of these compounds can also help you extend their anti-inflammatory, blood pressure lowering, and cardioprotective action.
Quercetin is arguably the most well-known bioflavonoid. Here is one of the highest-rated quercetin supplements on iHerb:

- 60 capsules; 500 mg per capsule
- Non-GMO, no artificial additives
This top-rated dietary supplement features high quantities of flavanones from citrus fruits:
Citrus Bioflavonoids Plus Hesperidin by Natural Factors

- 90 Capsules; 650 mg per capsule
- Additionally features hesperidin — the antioxidant compound found in citrus fruits
If you want to maximize your daily intake of anthocyanins, use this supplement:
Bilberry + Grapeskin Polyphenols by Jarrow Formulas

- 120 capsules
- Swedish bilberry (a wild European variety of blueberry that is especially rich in anthocyanins) + grape skin extract
- Vegan
What Are the Side Effects of Flavonoids
If you receive flavonoids from plant-based food, risks of flavonoid overdose and resulting adverse effects are negligible. You simply cannot overdose on flavonoids if you use food sources.
Bioflavonoids you receive from dietary supplements were also demonstrated to be generally safe in low to medium doses:
- Clinical studies have shown that oral intake of quercetin glycosides at doses up to 1000 mg/day for a period of up to three months did not cause any significant adverse effects. Still, very high daily doses (3,591 mg of quercetin) were linked to kidney toxicity;
- A 2015 study revealed that the consumption of 2 g of cocoa flavan-3-ols on a daily basis for a duration of 12 weeks was well tolerated and had no harmful side effects;
- In clinical trials some patients who took high doses (6 g/day) of caffeinated green tea extracts, reported mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal side effects. In another study where patients used decaffeinated green tea extracts (800 mg/day), mild gastrointestinal side effects were also observed in some people.
It is currently unclear whether flavonoid supplements are safe to consume during pregnancy and lactation. To be on the safe side, if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, only use flavonoid-rich foods which are totally safe for your health.
It is believed that flavonoid supplements can (theoretically) inhibit the action of anticancer drugs, and, if they are taken with anticoagulant drugs like warfarin, increase the risk of bleeding. For this reason, if you have a chronic health condition, it is recommended that you consult with your doctor before using any flavonoid supplements.
Flavonoids are known to bind nonheme iron (a type of iron found in plant foods, dairy products, and dietary supplements) and inhibit its absorption in the intestine. There are studies that demonstrate that one cup of such flavonoid-rich beverages as tea or cocoa can decrease the absorption of nonheme iron by about 70%. What’s more, flavonoids can also inhibit heme iron (one you get from meat) absorption.
For this reason, to maximize the amount of iron you get from meals or iron supplements, do not consume flavonoid supplements and flavonoid-rich food and beverages at the same time.
FAQ
In this section you will find the answers to some commonly asked questions about bioflavonoids.
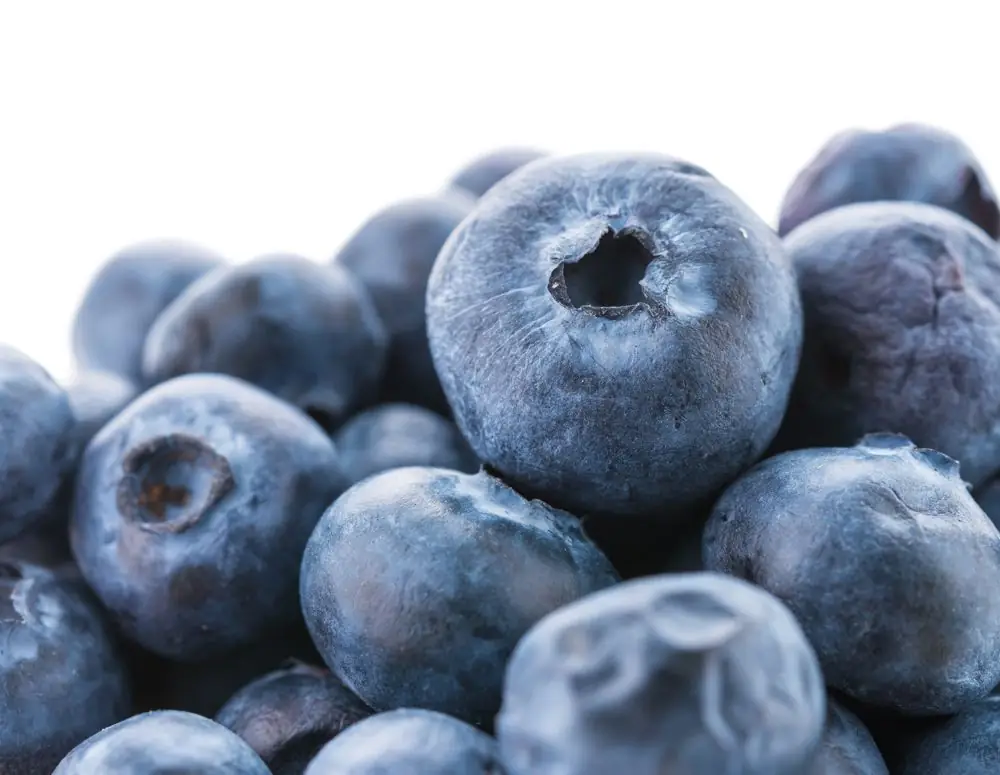
How Many Flavonoids Are in Blueberries?
Rich in manganese and vitamins C and K, blueberries are also an extremely good source of bioflavonoids: they contain both anthocyanins (163,5 mg per 100 grams) and flavan-3-ols (51,7 mg per 100 grams). Blueberries make an excellent snack and are very easy to incorporate into your diet.

What Are Flavonoids Found in Green Tea?
Green tea is an extremely good source of a subclass of flavan-3-ols called catechins. While black tea is also rich in catechins (on average, 115.3 mg per 100 grams), green tea is made from unoxidized leaves of the same plant, so its antioxidant and catechin content is significantly higher (on average, 203 mg per 100 grams).
What’s more, if you want to get as high an amount of catechins as possible, you can use matcha. Matcha comes from Japan: it is a powdered form of green tea that is extremely high in catechins.
Here is one of the highest rated Matcha teas on iHerb:
Matcha Green Tea Powder by MRM Nutrition

- 170 g (6 oz)
- Vegan & Non-GMO
A large-scale 2006 study conclusively proves that people who drink at least 5 cups of this beverage per day have a longer life expectancy.

How Much Flavonoids Are in Dark Chocolate?
If you want to know how many varieties of flavonoids are in cocoa powder, the answer is simple: cocoa only contains one flavonoid variety, namely, catechins (a subclass of flavan-3-ols). Still, the catechin content of cocoa is extremely high (on average, 243.2 mg per 100 grams).
Dark chocolates that feature considerably higher concentrations of cocoa are a much better choice if you want to get as many flavonoids as you can: on average, dark chocolate features 50.0 mg of catechins per 100 grams, while milk chocolate only offers 14.2 mg of catechins per the same quantity.
Here is one of the highest-rated dark chocolates on iHerb:
Strong + Velvety Dark Chocolate by Endangered Species

- 85 grams (3 oz)
- Whopping 88% cocoa
- Non-GMO & Fairtrade
- Vegan & kosher
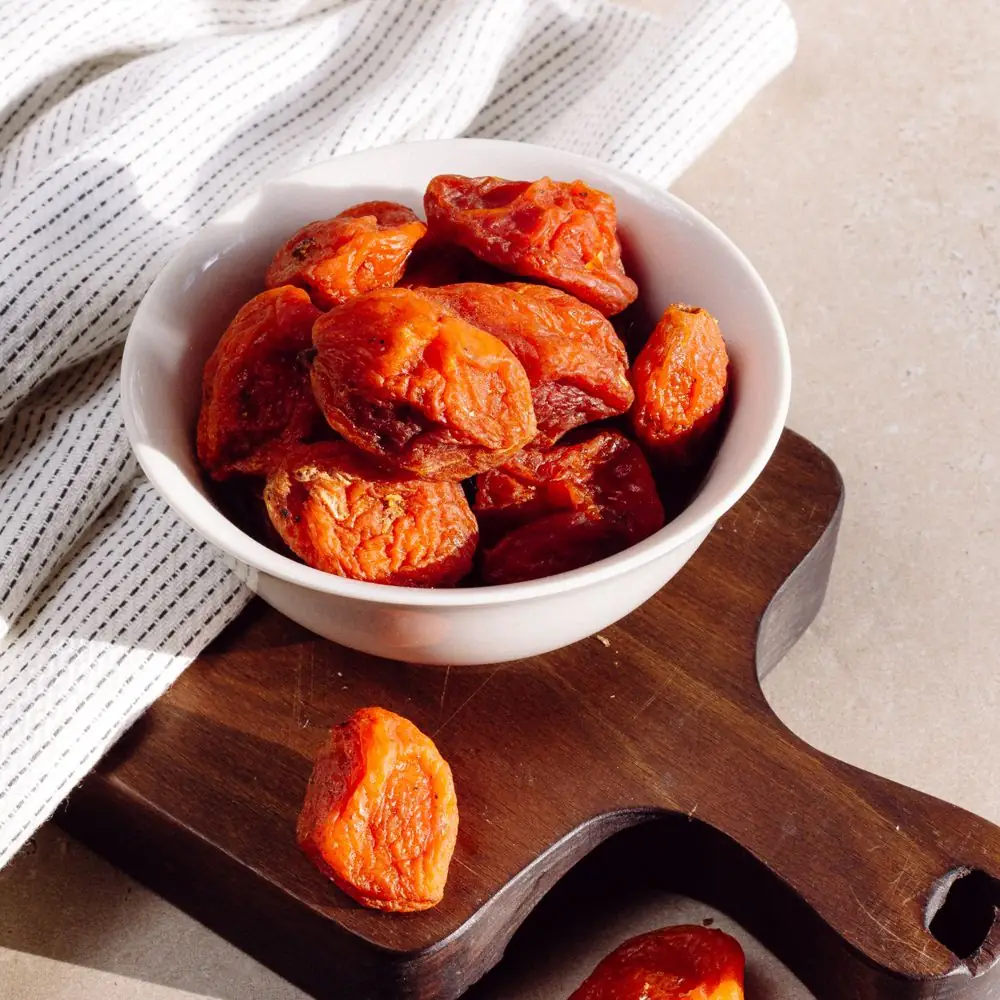
What Are the Differences Between Carotenoids and Flavonoids?
Carotenoids are natural pigments that give some plants their distinctive yellow, orange, or red color (carotenoids can be found in such foods as carrots, pumpkins, and apricots). Flavonoids (especially anthocyanins) make plants appear purple, blue, red, and black.
While, chemically speaking, these two classes of organic pigments are unrelated, both carotenoids and flavonoids are known to prevent the onset of cancer and act as antioxidants. Carotenoids are also extremely beneficial for eyesight and skin health.
Dried apricots are an excellent source of carotenoids (especially beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A) as well as vitamin E, B vitamins, potassium, iron, phosphorus, manganese, and magnesium. Use them as a healthy and nutritious snack between your meals.

How Do Flavonoids Kill Bacteria?
While plants use bioflavonoids to fight off various pathogens, and these compounds are known to reduce inflammation, they do not kill bacteria that are harmful to people. So, you cannot use them to treat bacterial infections.
What Does Consumption of Flavonoids Do for the Body?
In short, bioflavonoids:
- fight free radicals and delay aging;
- reduce blood pressure;
- decrease the risk of a cardiovascular event;
- reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes;
- prevent the development of certain types of cancer.

Now you know what’s flavonoids and what foods are rich in these healthy compounds. Keep in mind, though, flavonoids alone are not enough for wellness: it is important that you exercise regularly and enjoy a balanced diet.