What Are Types of Food High in Fiber: In-Depth Review
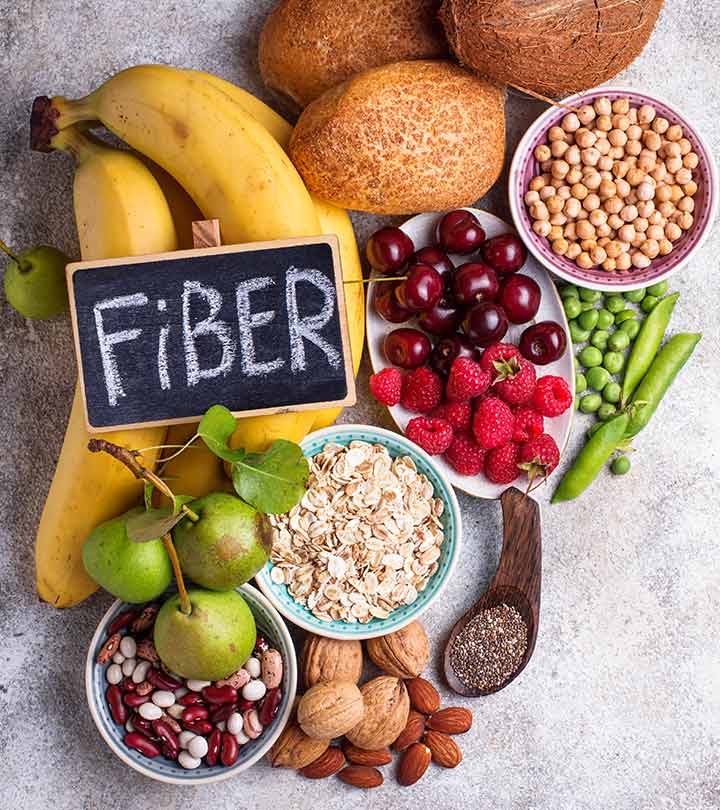

Dietary fiber is absolutely essential for your health. What are the food types high in fiber? Which of them are also low in calories and rich in vitamins and essential minerals? Which of them you can use for breakfast?

Read on, and you will find the answers to all these and numerous other questions.
What Kinds of Food Are High in Fiber
While all plant foods contain measurable quantities of dietary fiber (DF), some of them are true superstars.
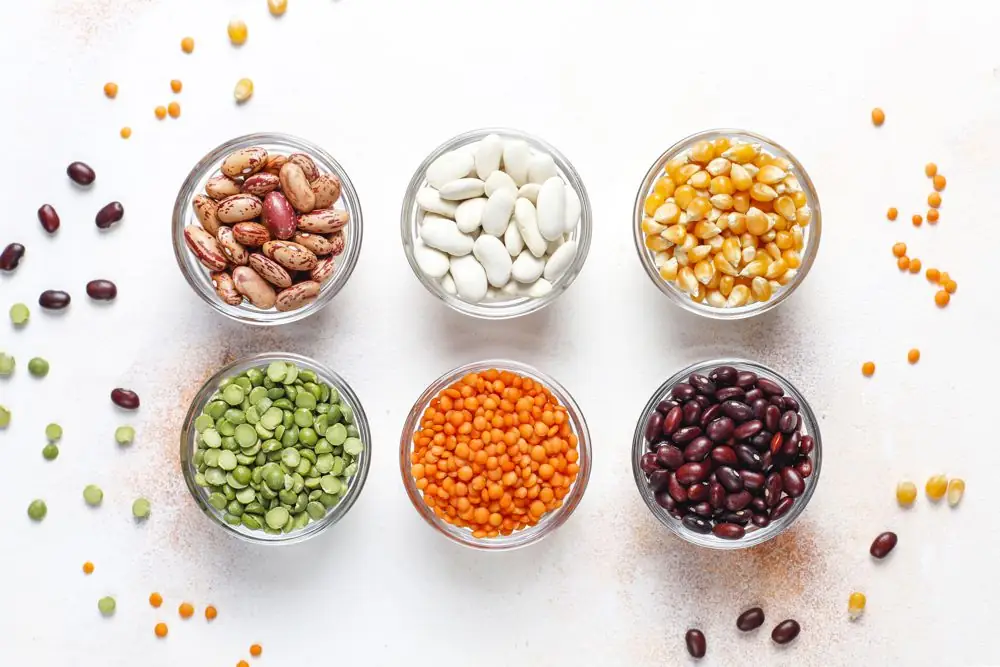
Legumes
Legumes in general are an excellent source of protein, vitamins, and dietary fiber. Here are the best choices you can make.
- Navy beans: contain whopping 10.5 grams of DF per 100 grams which is 27.6 percent of adequate daily intake (DI) for adult men. What’s more, if you wonder what are foods high in fiber and protein, navy, pinto, and black beans are exactly what you need. (See the table below to find out the exact figures for the fiber content and the percentage of daily intake for all other foods).

- Pinto beans: these beans are also extremely rich in vitamin B6 and folate (vitamin B9) and contain significant amounts of manganese, phosphorus, iron, magnesium, and zinc.
- Black beans: consume them with rice to get all 9 essential amino acids: they are also a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, and iron.
- Lentils: very rich in B vitamins and all kinds of dietary minerals, including copper, this food offers massive quantities of DF and is very easy to include in your diet. What’s more, if you wonder what foods are high in fiber and iron, lentils are one of the better answers as they contain 25% of DI of iron per 100 grams.
- Chickpeas: contain huge quantities of folate, manganese, phosphorus, and iron.
- Kidney beans: offer lots of iron, phosphorus, zinc, and folate.
- Green peas: if you wonder what food is high in fiber and vitamin C, green peas are one of the better choices as they offer an incredible 40% of DI of vitamin C per 100 grams. What’s more, green peas are also a very good source of B vitamins and such dietary minerals as manganese, phosphorus, zinc, and iron.

Vegetables
While legumes are incomparable when it comes to protein content, vegetables are an excellent choice if you want to enjoy a balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and water. What’s more, if you wonder what foods are high in fiber and low in fat, vegetables will be the best possible choice. Here are some examples of vegetables that are very rich in DF:
- Carrots: pleasantly sweet, they feature copious amounts of vitamin A precursor called beta carotene. Boiled carrots are slightly richer in DF than raw ones: use them for your soups and eat them on their own.
- Beets: rich in folate and manganese, this root vegetable also contains large quantities of nitrate that your body uses to produce nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is a compound that is essential for blood pressure normalization.

- Broccoli: this well-known vegetable also contains huge quantities of vitamins C and K and noticeable amounts of B vitamins and manganese.
- Artichokes: ideal for salads, they feature measurable quantities of folate, vitamin K, magnesium, and phosphorus.
- Sweet potatoes: this vegetable, which is often erroneously called ‘yams’, offers high quantities of vitamins A, C, and B6 as well as manganese and potassium.
- Brussels sprouts: this small cabbage is the right choice if you want to get copious amounts of vitamins C and K. It is also rich in manganese, phosphorus, and B vitamins.
- Kale: this food is extremely rich in vitamins C and K, features copious quantities of B vitamins, and will be an excellent choice if you want to increase your manganese intake.
- Cabbage: rich in vitamins K and C and a good source of folate and manganese, cabbage also contains copious amounts of water. Its crunchy leaves are impossible not to like!

Fruits
Fruits make an ideal snack that can be eaten between meals. Here are the fruits that are not only rich in vitamins and water but also feature massive amounts of DF.
- Avocado: a good choice when it comes to dietary minerals, it is very rich in B vitamins and DF.

- Prunes: extremely rich in DF, prunes are also great sources of B vitamins, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. What’s more, if you want to know what foods are high in fiber to help with constipation, look no further than prunes, as they are a traditional and time-tested remedy for constipation.
- Pear: full of sweet juice, pears are an excellent source of DF. If you wonder what are high fiber foods for adults and children alike, pears are one of the better choices: everyone just loves them.
- Raspberries: they are very rich in vitamin C and manganese, and their delicate taste is impossible not to like.
- Apples (with skin): whichever apples you like better — crunchy, tangy, or sweet — they are an excellent way to boost your daily DF intake.
- Bananas: rich in vitamins B6 and C, bananas are also a good source of manganese, magnesium, and potassium.
- Strawberries: this delicious fruit is an excellent source of vitamin C and manganese.
- Oranges: sweet and rich in vitamin C, oranges also contain measurable quantities of B vitamins, including folate.

Nuts & Seeds
If you wonder what foods are high in fiber and suitable for breakfast, nuts, and seeds are an obvious answer. Rich in calories, they can help you stay energetic till lunch. Here are the nuts and seeds that contain huge quantities of DF and can be consumed every day:
- Chia seeds: not only are chia seeds in a league of their own when it comes to the DF content, but they are also extremely rich in vitamins B1 and C as well as in such dietary minerals as calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc.
- Almonds: in addition to being very rich in DF, these healthy nuts are also an excellent source of B vitamins, vitamin E, manganese, magnesium, copper, iron, and phosphorus.
- Pistachios: extremely high in vitamin B6, this food is also a good choice if you want to boost your manganese and phosphorus intake.
- Sunflower kernels: sunflower seeds are an excellent source of vitamins E and B6; they are also very rich in folate, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, iron, and zinc.
- Pumpkin seeds: rich in B vitamins, they also contain copious quantities of iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc.

Grains
Use grains to feel fuller after your meals. If you want to know what dinner foods are high in fiber, grains are really what you need. Here are some grains that are extremely rich in DF.
- Buckwheat: while technically speaking buckwheat is a seed, not a grain, it looks very much like grain to most people. Buckwheat is very rich in B vitamins as well as magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and copper. Another important benefit of this food is that it contains no gluten.
- Quinoa: this trendy food is a good source of folate, vitamin B6, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc.
- Brown rice: brown rice is rich in DF because of its bran and germ layers (the better-known white variety is basically the same food but with these important sources of DF removed). It is a very good source of B vitamins, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium.
- Oatmeal. When discussing foods high in fiber, oatmeal is impossible not to mention. Always choose the steel-cut variety (also called coarse oats) because it is considerably richer in DF compared to white oats.
- Whole-wheat bread. This food helps you stay full for a longer time; it is also a good source of plant protein.

Foods High in DF with Grams per Average Serving: A Table
In the table below you will find foods high in fiber with grams per average serving and percentage of daily intake for an adult man. The foods are listed in descending order of daily intake of DF per serving.
| Food | 100 grams | Average serving | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF, g | Daily intake of DF per 100 g, % | Serving size | DF, g | Daily intake of DF per serving, % | |
| Oatmeal (steel-cut, coarse oats) | 12 | 31.6 | 1 cup (230 g) | 27.6 | 72.6 |
| Navy beans | 10.5 | 27.6 | 1 cup (182 g) | 19.1 | 50.3 |
| Black beans | 8.7 | 22.9 | 1 cup (180 g) | 15.7 | 41.2 |
| Lentils | 7.9 | 20.8 | 1 cup (198 g) | 15.6 | 41.2 |
| Pinto beans | 9 | 23.7 | 1 cup (171 g) | 15.4 | 40.5 |
| Chickpeas | 7.6 | 20.0 | 1 cup (164 g) | 12.5 | 32.8 |
| Kidney beans | 6.4 | 16.8 | 1 cup (187 g) | 12.0 | 31.5 |
| Raspberries | 6.5 | 17.1 | 1 cup (123 g) | 8.0 | 21.0 |
| Green peas (fresh, shelled) | 5.1 | 13.4 | 1 cup (145 g) | 7.4 | 19.5 |
| Chia seeds | 34.4 | 90.5 | 1.5 tablespoons (20 g) | 6.9 | 18.1 |
| Artichokes (raw) | 5.4 | 14.2 | 1 medium (125 grams) | 6.8 | 17.8 |
| Avocado | 6.8 | 17.9 | 1 average, without skin and seed (100 g) | 6.8 | 17.8 |
| Prunes | 7.1 | 18.7 | ½ cup (80 g) | 5.7 | 14.9 |
| Pear | 3.1 | 8.2 | 1 medium (170 g) | 5.3 | 13.9 |
| Quinoa | 2.8 | 7.4 | 1 cup (180 g) | 5.0 | 13.3 |
| Buckwheat | 2.7 | 7.1 | 1 cup (170 g) | 4.6 | 12.1 |
| Sweet potatoes (boiled) | 2.5 | 6.6 | 1 large (180 grams) | 4.5 | 11.8 |
| Apple (with skin) | 2.4 | 6.3 | 1 large (170 g) | 4.1 | 10.7 |
| Almonds | 11.8 | 31.1 | 25 nuts (30 g) | 3.5 | 9.3 |
| Carrots (raw) | 2.8 | 7.4 | 1 large (124 grams) | 3.5 | 9.1 |
| Brown rice | 1.8 | 4.7 | 1 cup (190 g) | 3.4 | 9.0 |
| Banana | 2.6 | 6.8 | 1 large (130 g) | 3.4 | 8.9 |
| Brussels sprouts (raw) | 3.8 | 10.0 | 1 cup (88 g) | 3.3 | 8.8 |
| Strawberries | 2 | 5.3 | 1 cup (160 g) | 3.2 | 8.4 |
| Whole-wheat bread | 7 | 18.4 | 1 slice (43 g) | 3.0 | 7.9 |
| Pistachios | 10.3 | 27.1 | 1 ounce or 49 kernels (28 g) | 2.9 | 7.6 |
| Orange | 2.4 | 6.3 | 1 medium, peeled and de-pithed (120 g) | 2.9 | 7.6 |
| Beets (boiled) | 2 | 5.3 | 1 cup (136 g) | 2.7 | 7.2 |
| Sunflower kernels | 8.6 | 22.6 | ¼ cup, shelled (28 g) | 2.4 | 6.3 |
| Broccoli (raw) | 2.6 | 6.8 | 1 cup (91 g) | 2.4 | 6.2 |
| Cabbage (raw) | 2.5 | 6.6 | 1 cup, chopped (89 g) | 2.2 | 5.9 |
| Kale (raw) | 2 | 5.3 | 1 cup (67 g) | 1.3 | 3.5 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 3.9 | 10.3 | 1 ounce (28 g) | 1.1 | 2.9 |
FAQ
In this section you will find the answers to the most common questions about dietary fiber.
What Is Fiber?
Dietary fiber refers to the indigestible carbohydrates present in plant foods. Although your body cannot digest DF, it plays a vital role in maintaining your overall health. There are two types of DF: soluble and insoluble. While soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance, insoluble one cannot be dissolved in water.

How Can DF Improve Your Health?
Fiber offers numerous health benefits, such as:
- Promoting a healthy weight. As DF cannot be digested, it helps you feel fuller for a longer time. What’s more, foods that are rich in DF are usually lower in calories.
- Reducing cholesterol levels. Daily consumption of such DF-rich foods as beans was linked to lower cholesterol levels: it is believed that DF reduces cholesterol absorption.
- Adding bulk to the digestive tract. DF makes your stool heavier and bulkier, which effectively stimulates the intestines and allows you to enjoy regular bowel movements.
- Acting as a prebiotic. Good bacteria that live in your gut and aid gastrointestinal health feed on DF.
- Promoting blood sugar control. Foods that are high in DF take a longer time to be broken down: this helps your blood sugar levels remain consistent. Avoiding so-called spikes in blood sugar is especially important for people with diabetes and those who were diagnosed with pre-diabetes.
- Reducing gastrointestinal cancer risk. There are recent studies that demonstrate that fiber-rich foods can protect against several types of cancer, including colon cancer. Some fibers (like pectin in apples) are believed to have antioxidant-like properties.
Dr. Megan Rossi says:
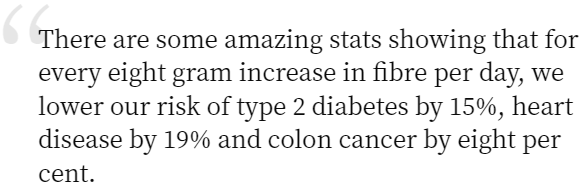
How Much DF Should I Consume Per Day?
It is recommended that for every 1,000 calories you get daily, you also consume at least 14 grams of DF. This equals about 38 grams of DF for adult men and 25 grams of DF for adult women. Unfortunately, even in such a developed country as the USA, nearly 95% of adults and children get considerably lower quantities of fiber than they ought to: the average DF intake in America is believed to be 16.2 grams.

How Can I Increase My Dietary Fiber Consumption?
First of all, try to include as many foods listed above in your diet as possible. What’s more, follow these tips:
- Do not peel your vegetables as their skins are usually very rich in DF;
- Use wholemeal bread instead of white bread;
- Use brown rice instead of white rice;
- Use rolled (or steel-cut) oats instead of instant oats;
- Eat at least 2 cups of fruit and 2-3 cups of vegetables each day;
- Use fiber supplements (psyllium husk is a good choice) if you cannot get enough DF through your diet.
Soluble DF makes up more than 70% of psyllium. This supplement is extremely easy to include in your diet: add it to your beverages, soups, and bakery, or use it instead of eggs.
Here is one of the more affordable psyllium supplements on iHerb:
Whole Psyllium Husks by NOW Foods

- 454 g (16 oz)
- 1-2 level tablespoon needs to be mixed with water (12 oz. or 350 ml)
- 6 grams of soluble DF per serving
And this supplement is ideal for adding to your food:

- 340 g (12 oz)
- Add 1 level tablespoon to water or juice (12 oz. or 350 ml)
- 38 servings per container
What Are High Fiber Vegetables and Fruits?
While all vegetables and fruits listed in the table above are rich in DF, avocados, prunes, raspberries, pears, artichokes, and sweet potatoes are foods that offer the highest quantities of fiber per single serving.
What Foods Are High in Fiber and Water but Low in Calories?
Water makes up more than 85 percent of an average apple’s weight, and this universally loved fruit is low in calories. Raspberries, artichokes, and carrots are also good examples of noncaloric foods that are high in DF.
What Are Foods High in Soluble Fiber?
Each type of DF has its benefits. It is believed that the gel that soluble fiber turns into can slow digestion and lower blood sugar, while insoluble fiber softens stool and makes it easier to pass.
There are numerous types of food that are rich in soluble fiber:
- oats
- peas
- various kinds of beans
- apples
- oranges
- carrots
- avocados
- sweet potatoes
- pears
- broccoli
- apples
- sunflower seeds.
Thus, if you are going to shed some pounds and want to slow down the rate at which your body absorbs calories, choosing the right food won’t be an issue.

What Foods Are High in Prebiotic Fiber?
While most prebiotics (i.e., compounds that feed good bacteria that live in your intestine) are a type of dietary fiber, not all fibers work as prebiotics. The most potent prebiotic fibers in our food include inulin, fructans, and galactooligosaccharides (GOS). Here are vegetables, fruits, grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes that are rich in these prebiotic fibers:
- artichokes,
- green peas,
- apples,
- oats,
- whole grain wheat,
- pistachios,
- all kinds of beans,
- chickpeas,
- lentils.

In general, it is always a good idea to add beans to your diet as not only are they extremely rich in fiber by sheer amounts, but they also feature a lot of soluble and prebiotic fiber.Now you know what are food types high in fiber. While DF is essential, do not neglect to take care of all aspects of your health: do not overindulge in caloric foods and exercise regularly.